Multimodal Transformer-Based Human Intent Recognition Using Skeleton and RGB Data for HRI Applications
Goal The objective of this study is to develop a multimodal Transformer-based classification model for human intent recognition by processing both skeleton and RGB data, aiming to improve accuracy in distinguishing human intents, particularly in HRI-relevant scenarios where skeleton data alone may be insufficient. ***
Summary
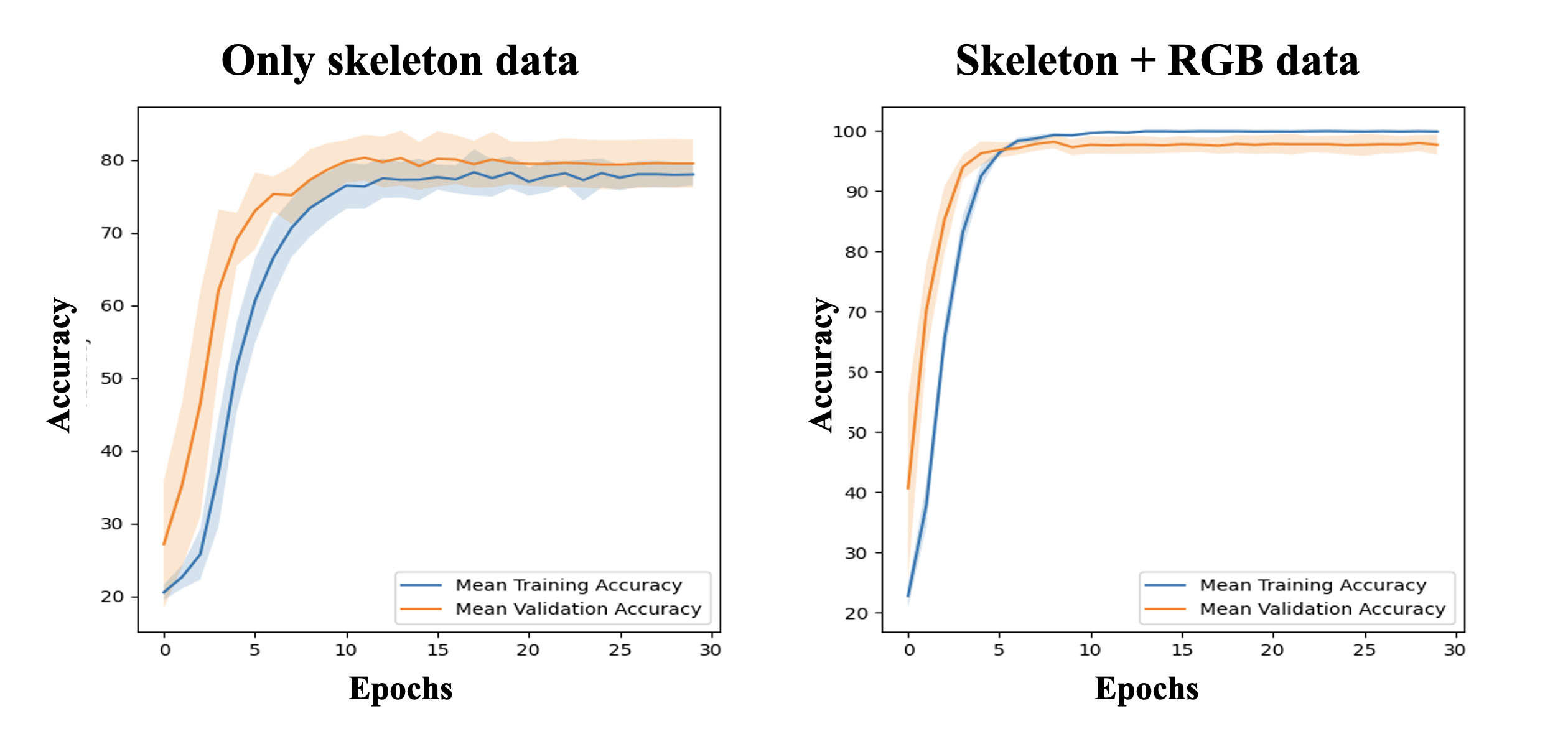
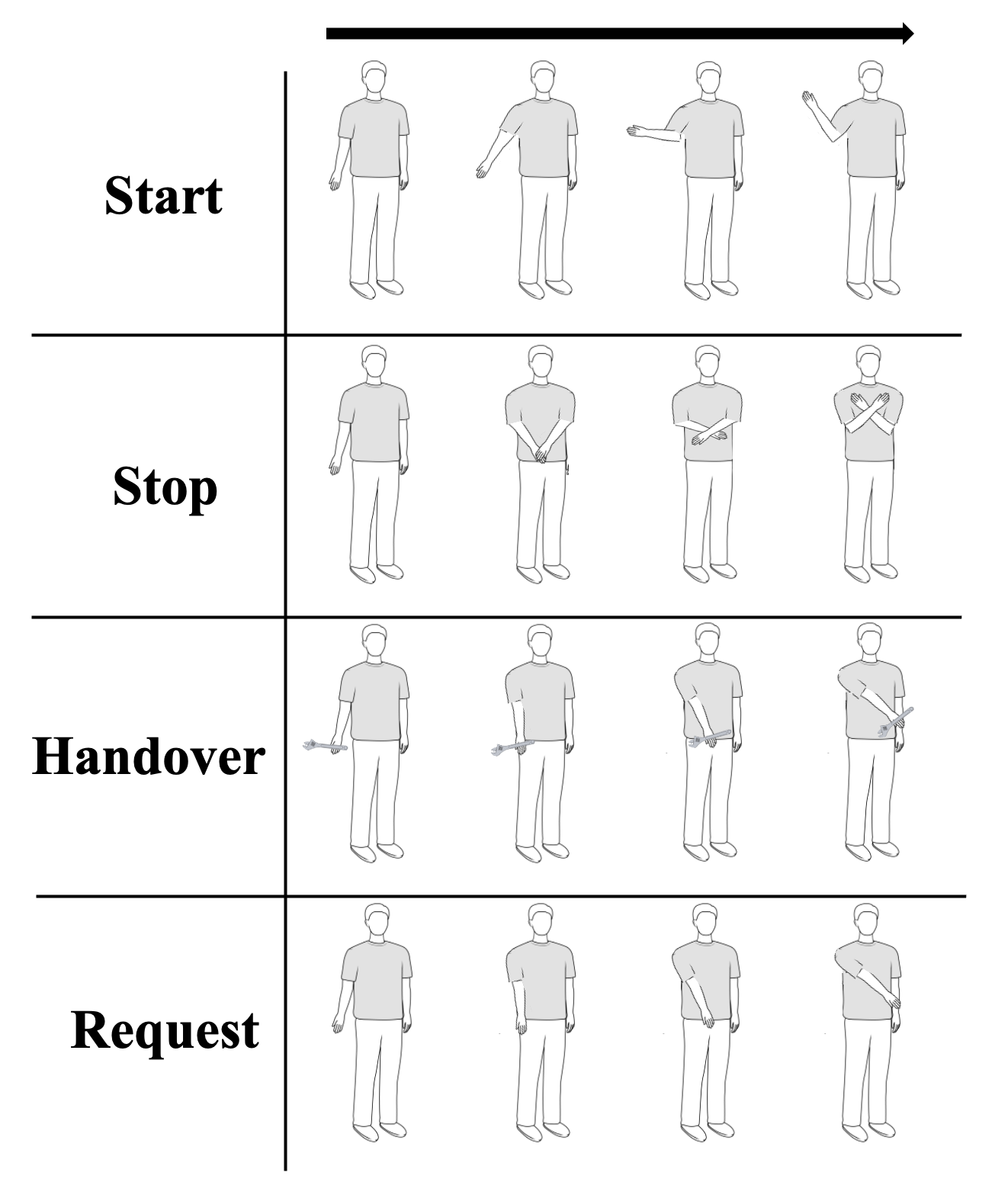
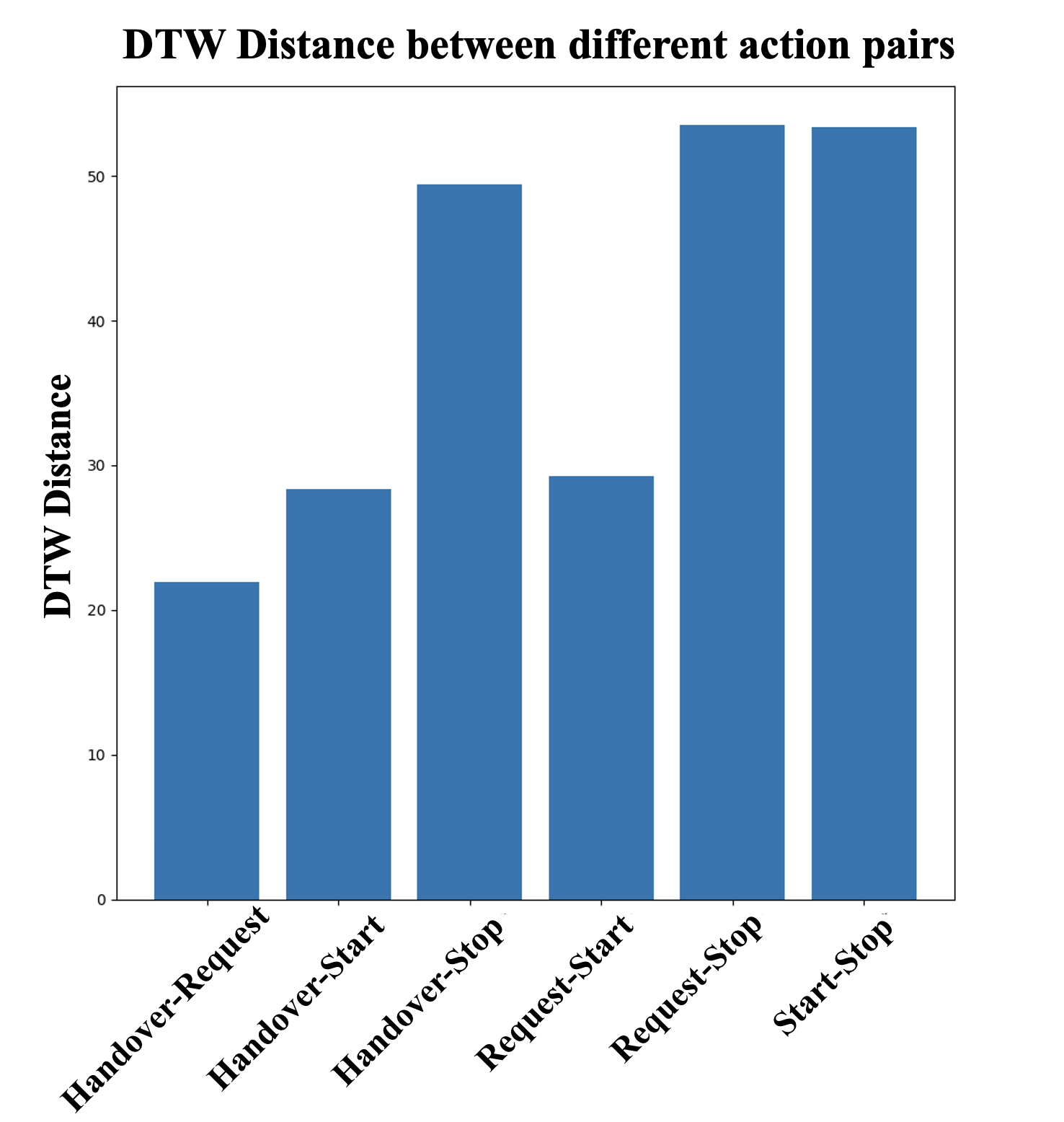
This study proposes a multimodal Transformer-based classification model for Human Intent Recognition (HIR) in Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) scenarios. The model integrates both skeleton and RGB data to enhance recognition accuracy, leveraging a Transformer encoder architecture with a Self-Attention Mechanism to effectively capture long-range dependencies in sequential input. By processing skeleton and RGB inputs in parallel, the model improves both computational efficiency and classification performance. Performance evaluations show that the skeleton-only model achieved an accuracy of 79.50±3.31%, while the multimodal model achieved 97.70±1.68%, clearly demonstrating the benefits of incorporating RGB data. These results were validated using ten different random seeds, and further confirmed by analyzing the confusion matrix of the best-performing model. Notably, the skeleton-only model struggled to distinguish between Handover and Request actions due to the similarity in joint movements, as revealed by a Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) analysis. In contrast, the multimodal model successfully differentiated these actions by utilizing additional visual features from the RGB data—such as objects held in the user’s hand—allowing for more precise intent classification. These findings highlight the effectiveness of the proposed multimodal approach in improving HIR accuracy and underscore its potential for building intuitive and reliable human-robot interaction systems.