Towards Ergonomics-based Human-Robot Collaboration with Intelligent Anticipatory Behaviours
2022-03-01 ~ 2027-02-28
Period : 2022-03-01 ~ 2027-02-28
Goal of This Project
Development of ergonomic human-robot collaboration technology that can predict human engineering status of workers in real time and improve risk factors through collaboration with robots.
To do this, this study established Five Scientific Objectives (SO)
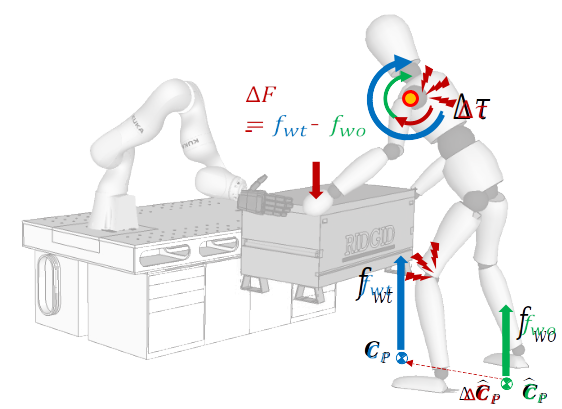
- (SO.1) : Understanding Human Engineering Risks in Dynamic Human-Robot-Environmental Interactions.
- (SO.2) : A Study on Human-Robot Collaboration Techniques to Prevent Musculoskeletal Diseases.
- (SO.3) : A Study on the Interface for Improving Human Engineering Elements Using Human Redundancy
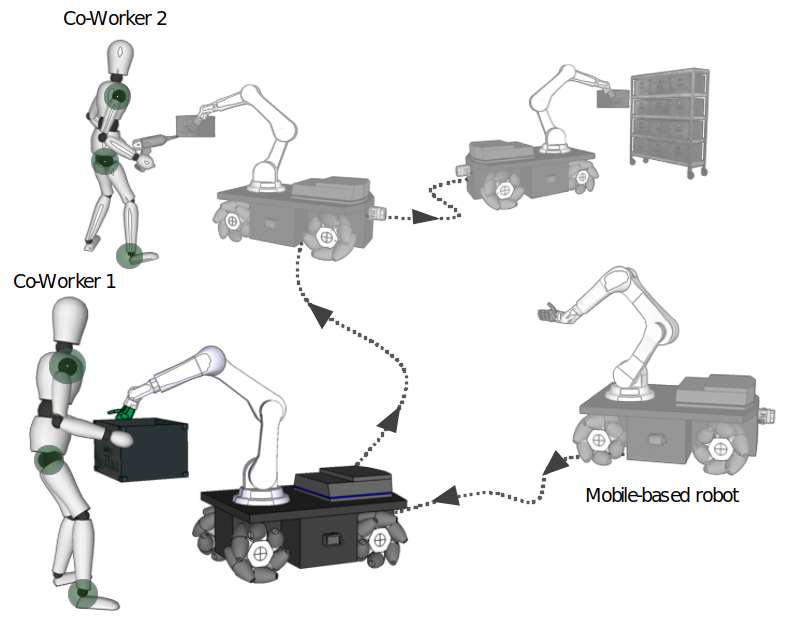
- (SO.4) : A Study on the Human-Robot Sharing Control Method Considering Priority
- (SO.5) : Validation of ergonomic human-robot collaboration techniques.
Project Contents
To achieve the Five Scientific Goals (SO) of this study, Five Work Package (WP) were established, and detailed research contents such as robotics, ergonomics, artificial intelligence, and statistics were classified by task according to each research plan.
- (WP.1) : Investigate and analyze the factors that cause musculoskeletal disease rates by presenting a ergonomic evaluation model in a dynamic interaction situation.
- (WP.2) : Eradicating/reducing hazardous or detrimental factors to the operator through ergonomic prediction/action control.
- (WP.3) : Implementation of a feedback interface to reflect the human body’s Redundancy behavior.
- (WP.4) : Behavior Prediction and Sharing Control Using Artificial Intelligence.
- (WP.5) : Integration of human-robot collaboration system considering human engineering,
Experiments on the developed ergonomic model,
Building an open database with sensor data.
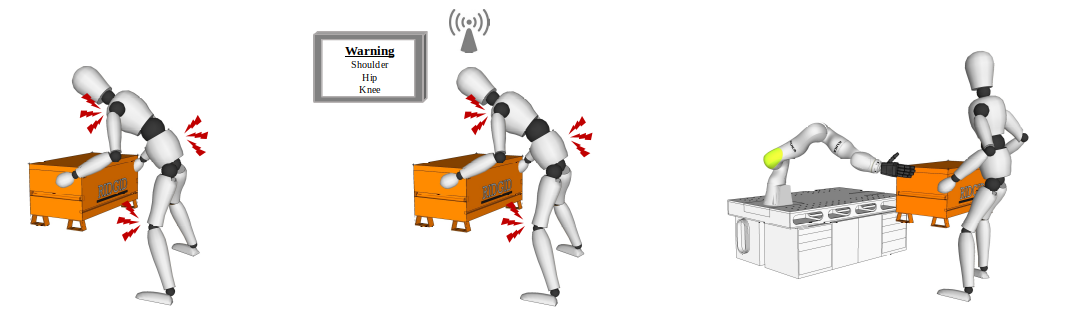
robot can control the robotic partner’s Assistive behavior to minimize the overloading Effects